Created: September, 1, 2023 Last Modified: September, 1, 2023
Cross Compiling C Code For Raspberry Pi Zero W
Getting The correct Toolchain
There a lot of different methods for getting a correct toolchain in order to cross compile.
You could build your own using something like crosstools-ng, yocto
or with buildroot.
But by far the easiest method is to use a prebuilt toolchain, Arm provides some as well as Bootlin.
In this post we are going to use one from bootlin (note this requires the host to be linux based), However first we need to find the version of glibc our target system is using.
Run ldd --version | grep GLIBC on the target machine (raspberry pi) you should get an output like this
root@pg3-pizerow:~/binaries# ldd --version | grep GLIBC
ldd (Debian GLIBC 2.31-13+rpt2+rpi1+deb11u5) 2.31
At the time of writing the raspberry is using Debian11 which comes with glibc 2.31.
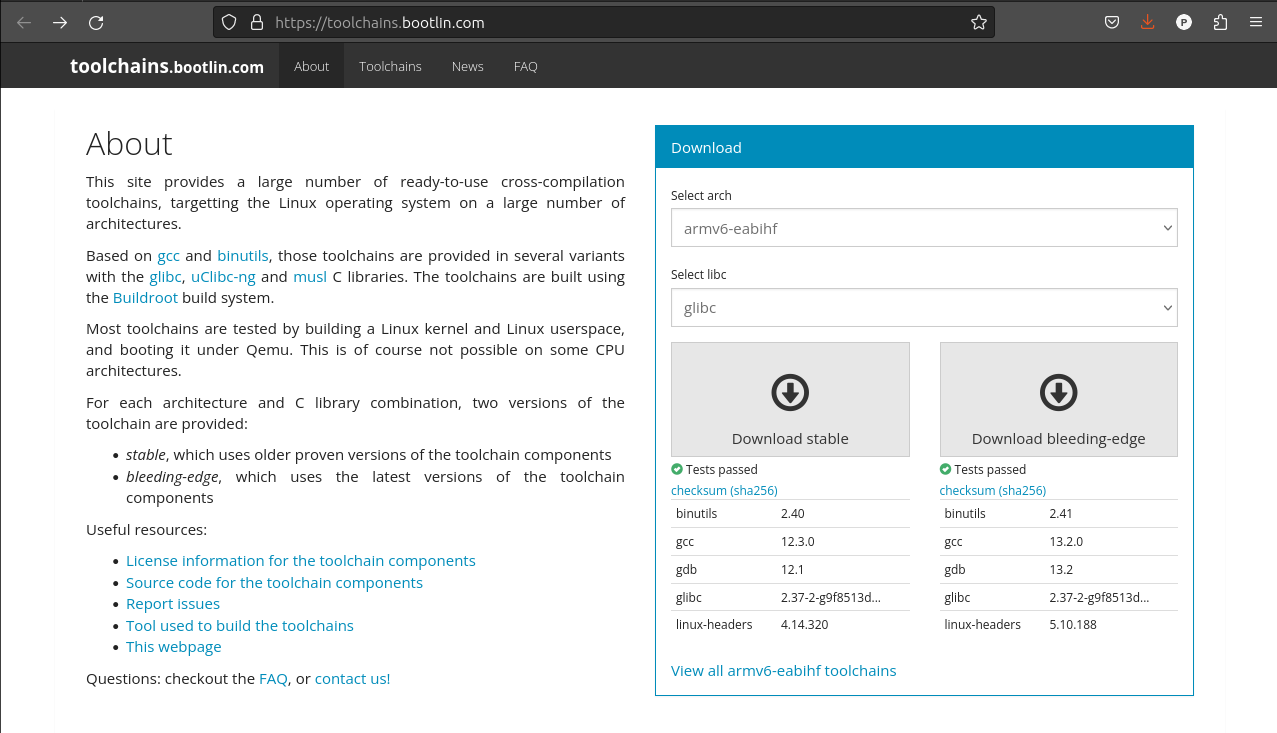
Now we need to go to Bootlins Toolchains and select the arch and libc we want to target.
In this case thats armv6-eabihf and glibc as shown below.
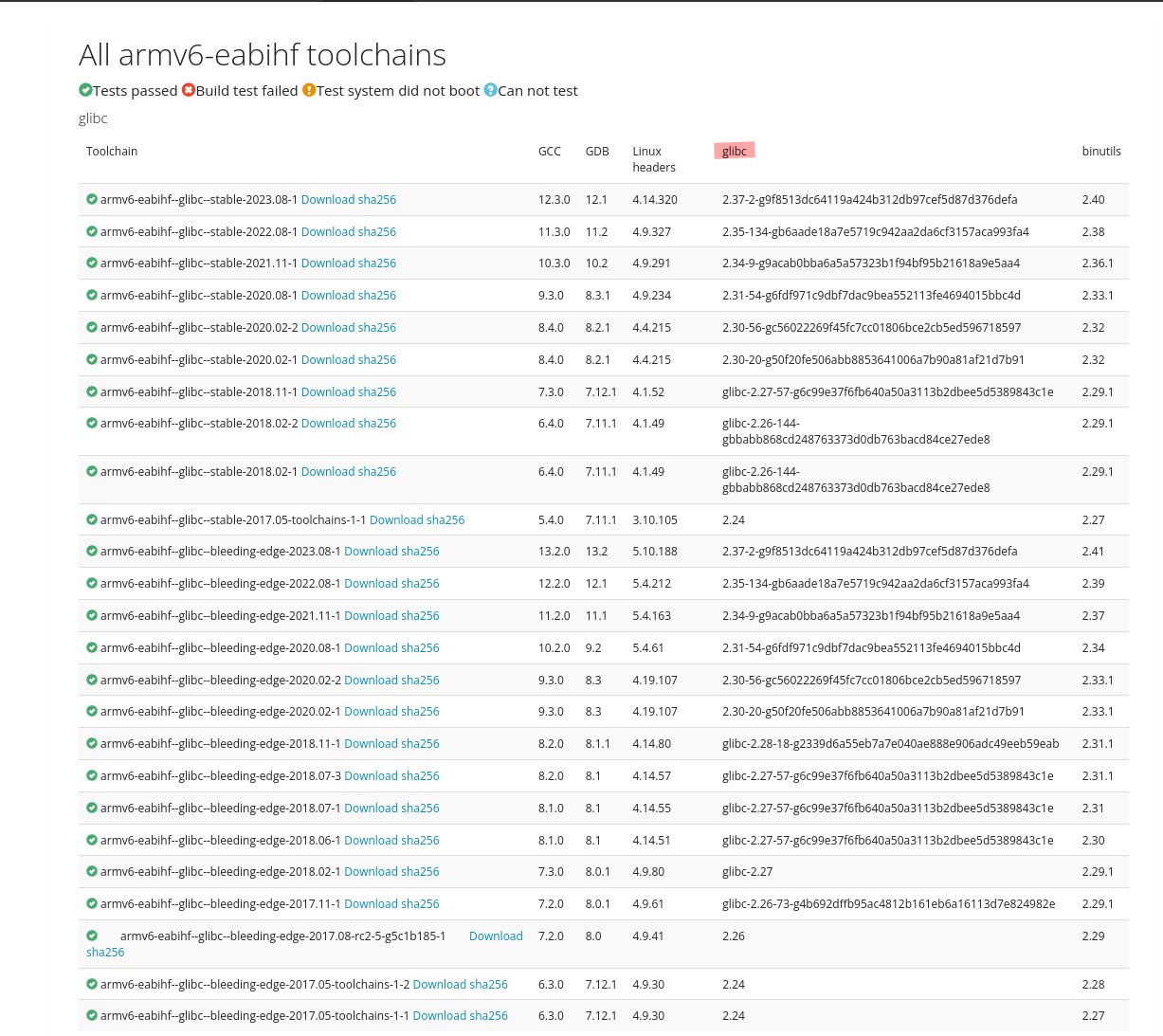
 Next Click on view all toolchains and we need to select the toolchain with the correct glibc. In this case we are looking for 2.31.
Next Click on view all toolchains and we need to select the toolchain with the correct glibc. In this case we are looking for 2.31.
 In this case
In this case armv6-eabihf--glibc--stable-2020.08-1 is the one we want.
Download the toolchain, move it the directory you want to store it in and extract it using tar -xvjf armv6-eabihf--glibc--stable-2020.08-1.tar.bz2.
For this example I will extract it next to my main.c file that I will build for demonstration, however you should put this in a path that can be easily accessed for other projects.
Also generally you want to add /dir_you_store_it_in/armv6-eabihf--glibc--stable-2020.08-1/bin to your path some how. Possibly by adding a line in your bashrc or by creating a script that you source to setup your build environment. In this case we are just going to use the direct path to arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf-gcc to build a simple c program.
Test C Program
Now lets create a basic C program to test that the compiler is working correctly. Create a main.c with the following contents.
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
printf("Hello World\n");
return 0;
}
Now we can compile the program using our cross compiler. Again for this demo Ill use the direct path to GCC which is store next to our main.c ./armv6-eabihf--glibc--stable-2020.08-1/bin/arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf-gcc however if you have it in your path you just need to use arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf-gcc.
To compile the program run
./armv6-eabihf--glibc--stable-2020.08-1/bin/arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf-gcc main.c -o c_cross
Now copy our program to the Pi, mine is network connected so I'll use scp
scp c_cross [email protected]:/root/binaries
Now login to the pi and run /root/binaries/c_cross (change the path to match where you stored the build program). If all was built correctly you should seem something like this
root@pg3-pizerow:~/binaries# /root/binaries/c_cross
Hello World
With that you now have a working cross compiler for your Raspberry Pi Zero W!